Signs
Causes
Diagnosis
Care Guide
Frequently Asked Questions
Your cat is losing hair and, quite honestly, smells like corn chips. You know it’s not normal, so you call your veterinary hospital to schedule an appointment. Your head is spinning after your veterinarian suggests a skin impression and diagnoses a Malassezia infection. What is that? Let’s take the mystery out of this skin infection.
What Is Malassezia Dermatitis?
Malassezia pachydermatis is a particular species of yeast. This organism usually lives in small numbers on your dog or cat’s skin and ears. However, it occasionally grows out of control, leading to skin or ear infections.
This species of yeast got its name from elephants or pachyderms. With severe or chronic Malassezia infections, your pet’s skin can thicken like leather or an elephant’s skin. Malassezia dermatitis differs from thrush in cats and is caused by Candida albicans.
What Are the Signs of Malassezia Dermatitis in Cats?
Cats with a Malassezia skin infection may present with a variety of signs. The cat may be itchy, ranging from mild to intensely pruritic. Your cat might also have an odor. Some people equate it to corn chips, but remember that other things, such as bacterial skin infections, can have a similar smell.
Often, the coat and skin of affected cats change. You might see:
- Hair loss (alopecia)
- Red skin or ears
- Lichenification of the skin, where it gets thick and leathery feeling
- Dry, flaking skin, with or without extra greasy skin
- Hyperpigmentation or darker coloring on areas like the bottom of the belly
- Crusting or brown staining around the nail beds
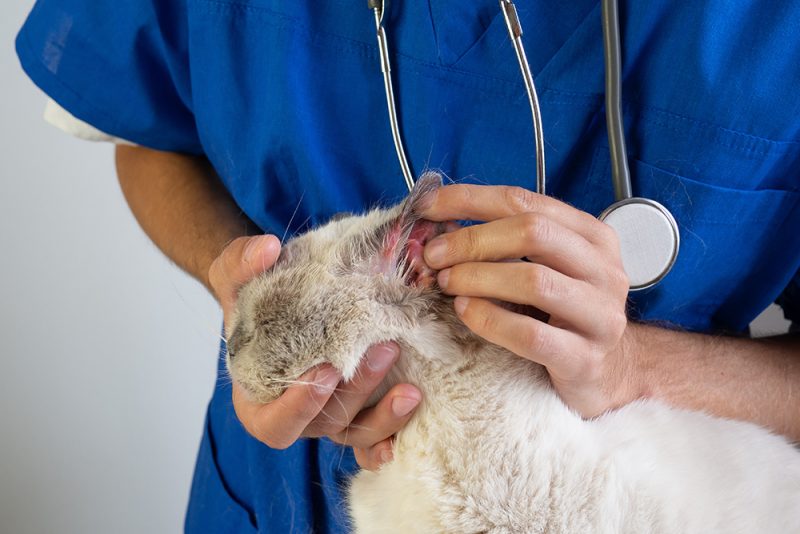
If your cat only has one or more of the following signs of Malassezia, it might be evidence of an ear infection.
- Dark, smelly discharge in one or both ears
- Red pinnae
- Scratches or broken hairs on the back of your cat’s pinnae
- Head tilt
Consulting a veterinarian is recommended for the best course of action.
If you need to speak with a vet but can’t get to one, head over to PangoVet. It’s an online service where you can talk to a vet online and get the personalized advice you need for your pet — all at an affordable price!
What Are the Causes of Malassezia Dermatitis in Cats?
Malassezia dermatitis generally occurs when a cat has a disruption of the normal skin barrier. Without your cat’s body’s normal protective mechanisms in place, your cat is at risk for yeast and even bacterial infections. Allergies are quite common in our kitties, just like they can be for people. Allergies in cats are usually divided into four main categories:
- Environmental
- Food
- Insect
- Contact
Allergies can make our cats itchy or pruritic, further disrupting the skin barrier. Metabolic conditions are sometimes associated with skin lesions and Malassezia infections. Hyperthyroidism in cats can lead to overgrooming.
Certain medications increase the likelihood of suppressing your cat’s immune system and make secondary infections more likely. A common medication category is steroids. Interestingly, steroids are also used to decrease skin inflammation. Chemotherapy medications can also affect the immune system.
Diagnosing Malassezia Dermatitis in Your Cat
If your cat has hair loss or lichenified skin, how exactly do we get a diagnosis and figure out what’s going on? First, your veterinarian will take a thorough history. Your vet will likely need to know things like:
- What foods does your cat eat?
- When was the last time you applied flea prevention?
- Have you used new laundry detergent?
Can you think of anything that might have changed in your cat’s environment? Make sure to let your veterinary team know. Your vet will examine your cat from nose to tail. They’ll need to look inside your cat’s ears, between your feline’s toes, and on the cat’s belly. Your veterinarian will look for evidence of fleas, broken hairs, scaly skin, or signs of an ear infection.
To diagnose Malassezia, your vet will generally utilize a skin cytology. They will take a glass microscope slide and collect smears from your cat’s skin, particularly places like the claw folds. The vet can also use a piece of tape to collect cells. The veterinary team stains the shoe and examines it under the microscope, looking for bacteria, yeast, and other cells.
Sometimes, your veterinarian will use other diagnostic tools. Blood work and a urinalysis are helpful to rule out metabolic issues like kidney disease and hyperthyroidism. A fungal culture is used to diagnose certain dermatophytes, which we commonly refer to as ringworm. A skin biopsy is used to diagnose conditions such as an autoimmune disorder.
How Do I Care for a Cat With Malassezia Dermatitis?
Topical therapy is the most commonly utilized treatment for Malassezia dermatitis, but oral medications are also used, especially in severe cases. Your veterinarian might prescribe topical spot-on medications like miconazole. Shampoos are helpful because they treat the infection and may help improve the skin barrier. By using topical medications like ketoconazole shampoo, you can get higher concentrations of the antifungal at the skin level where you need it.
Oral antifungal medications are helpful when you might have trouble treating an area topically. Unfortunately, these medications may have an increased rush of side effects, from causing inappetence to liver damage. If your cat needs to be on antifungal medication long-term, your veterinarian may need regular blood monitoring.
It’s important to treat the underlying cause of skin issues. Allergies may be treated with immunotherapy (allergy shots) or medications like Atopica (cyclosporine). For long-term control, you may need to use maintenance topical therapy or pulse-dosing oral medications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can you prevent Malassezia dermatitis?
It’s difficult to completely prevent a Malassezia infection because so many contributing factors exist. You can try to stay ahead of the problem with topical therapy, like antifungal shampoo or mousse. Omega-3 fatty acids are also helpful in strengthening your cat’s skin barrier.
Is Malassezia otitis the same as dermatitis?
Malassezia otitis is specifically an ear infection caused by an overgrowth of Malassezia. At the same time, dermatitis refers to an issue affecting the skin more generally.
Conclusion
Malassezia dermatitis may be less commonly diagnosed in cats than dogs, but it’s no less frustrating. Your veterinarian must diagnose the condition with a skin cytology and treatment may involve regularly bathing your cat or oral antifungal medication.
- Also see: Cat Yeast Infection vs. Ear Mites: Vet Reviewed Differences (With Pictures)
Featured Image Credit: Yekatseryna Netuk, Shutterstock